Ever struggled with turning on and off appliances or circuits at specific times? Imagine being able to automate these tasks, freeing you from manual switching. This is where a single-phase contactor wired with a timer comes in handy. By understanding the wiring diagram, you can harness the power of automation for various applications, from residential lighting control to industrial processes. Let’s delve into the world of contactors and timers, unraveling their intricacies and unlocking their potential.
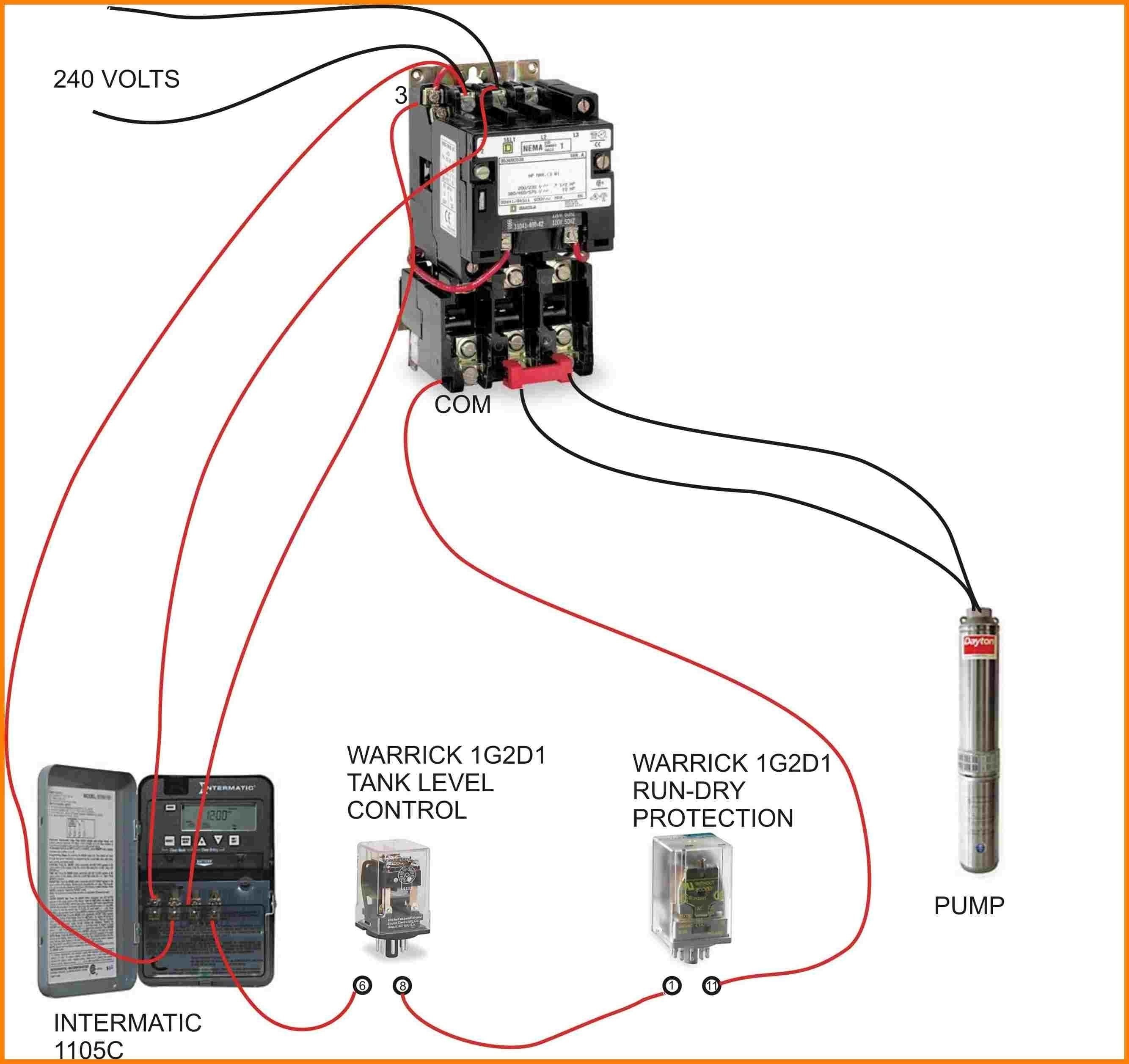
Image: manualfixsydney.z21.web.core.windows.net
Recently, I was tasked with automating the lighting system in my garage. I needed the lights to turn on at dusk and off at dawn, providing me with convenience and energy efficiency. After researching, I discovered the simplicity and effectiveness of a single-phase contactor paired with a timer. This setup allowed me to control the lighting system with a timed schedule, eliminating the need for manual intervention. In this article, we’ll explore the mechanics of this system, ensuring you can implement it successfully in your own projects.
Understanding Single-Phase Contactors and Timers
Single-Phase Contactor: The Power Switch
At its core, a single-phase contactor is an electrically controlled switch capable of handling high currents and voltages. It allows you to remotely control the flow of electricity to a load, like a motor or a lighting circuit. The contactor comprises three main parts:
- Coil: This electromagnetic component receives a low-voltage signal to control the contactor’s operation. When energized, the coil creates a magnetic field.
- Contacts: These are the physically moving parts that make or break the circuit between the power source and the load. They are usually made of silver or copper for excellent conductivity.
- Housing: The protective enclosure houses the contactor’s internal components, ensuring safe operation and preventing accidental contact.
Timer: The Timekeeper
A timer is an essential component for automating actions based on time. It can be analog or digital, offering various functionalities:
- On-delay timer: This timer delays the switching action after receiving a start signal, offering a time delay before turning a device on.
- Off-delay timer: This timer keeps the device on after the start signal is removed, offering a time delay before turning a device off.
- Cycle timer: This timer repeatedly cycles between on and off states, offering a recurring timer functionality.
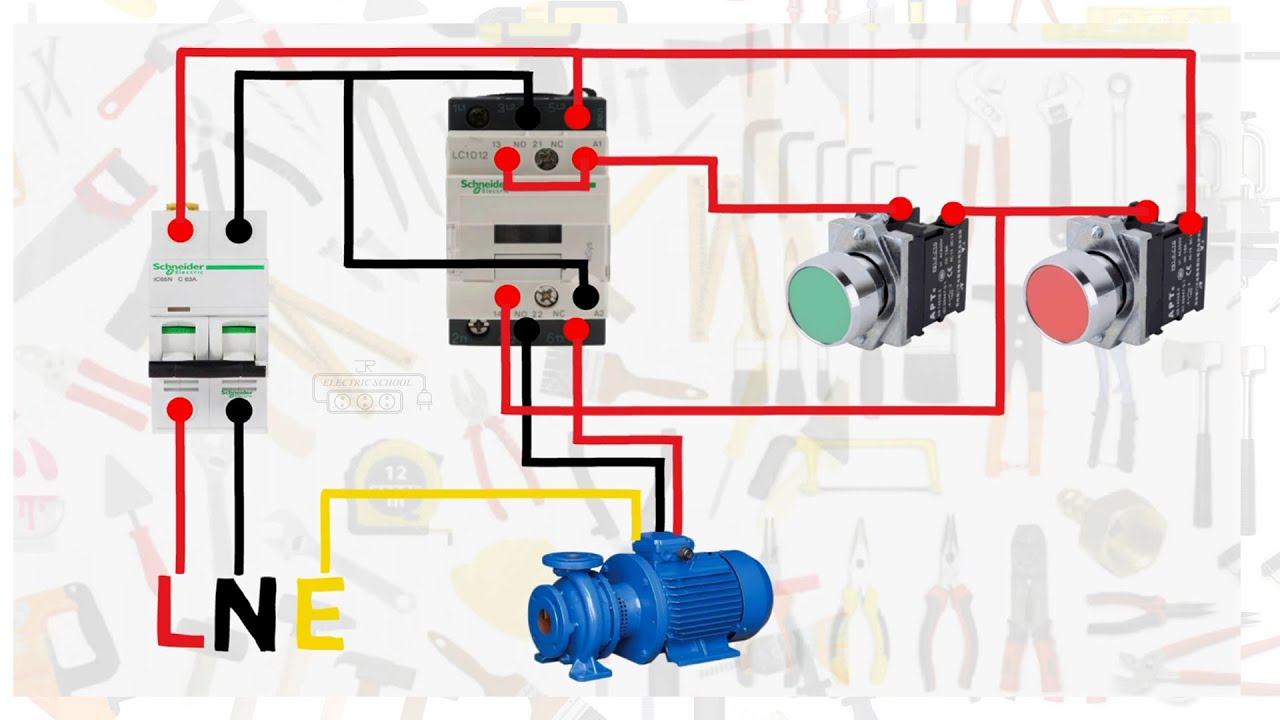
Image: schematicfixmaxima.z22.web.core.windows.net
The Importance of Understanding the Wiring Diagram
Before diving into wiring, understanding a single-phase contactor wiring diagram with a timer is crucial for safe and efficient operation. The diagram visually represents the electrical connections between each component. It helps you identify the power supply, control signals, and load connections, enabling you to correctly connect the contactor, timer, and the device you want to control.
Single-Phase Contactor Wiring Diagram with Timer: A Step-by-Step Guide
Let’s break down the wiring process, focusing on a common single-phase contactor wiring diagram with an on-delay timer:
1. Understanding the Components:
For this example, we’ll use a single-phase contactor with three main contacts (NO, NC, and common) and an on-delay timer with a single output.
2. Power Supply Connection:
Connect the power supply to the contactor terminals labeled “L1” and “L2.” These terminals receive the main power for the circuit.
3. Timer Supply Connection:
Connect the timer’s power supply terminals, typically labeled “L” and “N,” to a separate power supply branch. This ensures the timer operates independently from the contactor’s load.
4. Contactor Coil Connection:
Connect the timer’s output terminal to one side of the contactor coil. This output terminal typically provides a low-voltage signal controlled by the timer’s settings.
5. Coil Ground Connection:
Connect the other side of the contactor coil to the ground terminal.
6. Load Connection:
Connect the load (e.g., lights, motor) to the normally open (NO) contact of the contactor and the common terminal. Power will flow to the load when the contactor energizes its coil.
7. Timer Settings:
Configure the timer’s settings according to your desired on-delay time. This determines the delay before the timer activates the contactor coil.
Troubleshooting Tips and Expert Advice
When working with electrical components, safety is paramount. Always disconnect power before working on any wiring. Here are some tips to help you avoid common problems:
- Double-check your connections: Ensure all connections are secure and correctly wired before energizing the circuit.
- Use the right tools: Employ appropriate tools like wire strippers, crimpers, and terminal connectors for safe and reliable connections.
- Consult a qualified electrician: If you are unsure about any aspect of the wiring process, it’s best to consult a qualified electrician for professional guidance.
When troubleshooting your setup, consider the following:
- Check the power supply: Ensure the primary power source to both the timer and the contactor is functioning correctly.
- Verify timer settings: Ensure that the timer’s settings are correctly configured according to your desired on-delay time.
- Inspect the coil: Test the contactor coil for continuity to ensure it’s working properly. If necessary, replace the coil with a new one.
- Examine the contacts: Inspect the contactor’s contacts for signs of wear, corrosion, or dirt. Clean or replace them if necessary.
By following these tips, you can mitigate potential issues and ensure your single-phase contactor system operates effectively and reliably.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What voltage is typically used for a single-phase contactor coil?
A: Single-phase contactor coils commonly operate on 12V or 24VDC.
Q: Can I use a timer to control multiple loads with a single contactor?
A: Yes, you can wire multiple loads to the contactor’s NO contacts, allowing the timer to control all of them simultaneously. However, ensure the combined load doesn’t exceed the contactor’s amperage rating.
Q: What is the difference between a contactor and a relay?
A: A contactor is designed for high-current and high-voltage applications, often used to control motors and appliances. A relay is typically smaller and handles lower currents and voltages, often used in control circuits.
Q: What safety precautions should I take when working with single-phase contactors and timers?
A: Always disconnect power before working on any wiring. Use the appropriate tools and techniques to ensure safe and reliable connections. If unsure, consult a qualified electrician.
Single Phase Contactor Wiring Diagram With Timer
Conclusion
Understanding how to wire a single-phase contactor with a timer unlocks a world of automation possibilities. With this knowledge, you can create customized control solutions, from time-based lighting control to automated machinery operation. Remember to prioritize safety and double-check your connections before energizing the circuit. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently incorporate this reliable system into your projects, enhancing convenience, efficiency, and control.
Are you interested in learning more about specific applications for single-phase contactor wiring diagrams with timers? Let me know in the comments!






