Ever wondered why you inherit your mom’s eyes or your dad’s love for music? The answer lies within the intricate structure of DNA, the blueprint of life. It’s a molecule that holds the genetic code, dictating everything from your hair color to your susceptibility to certain diseases. Understanding the structure of DNA is like unlocking a secret code, revealing the profound mechanisms that make life possible.
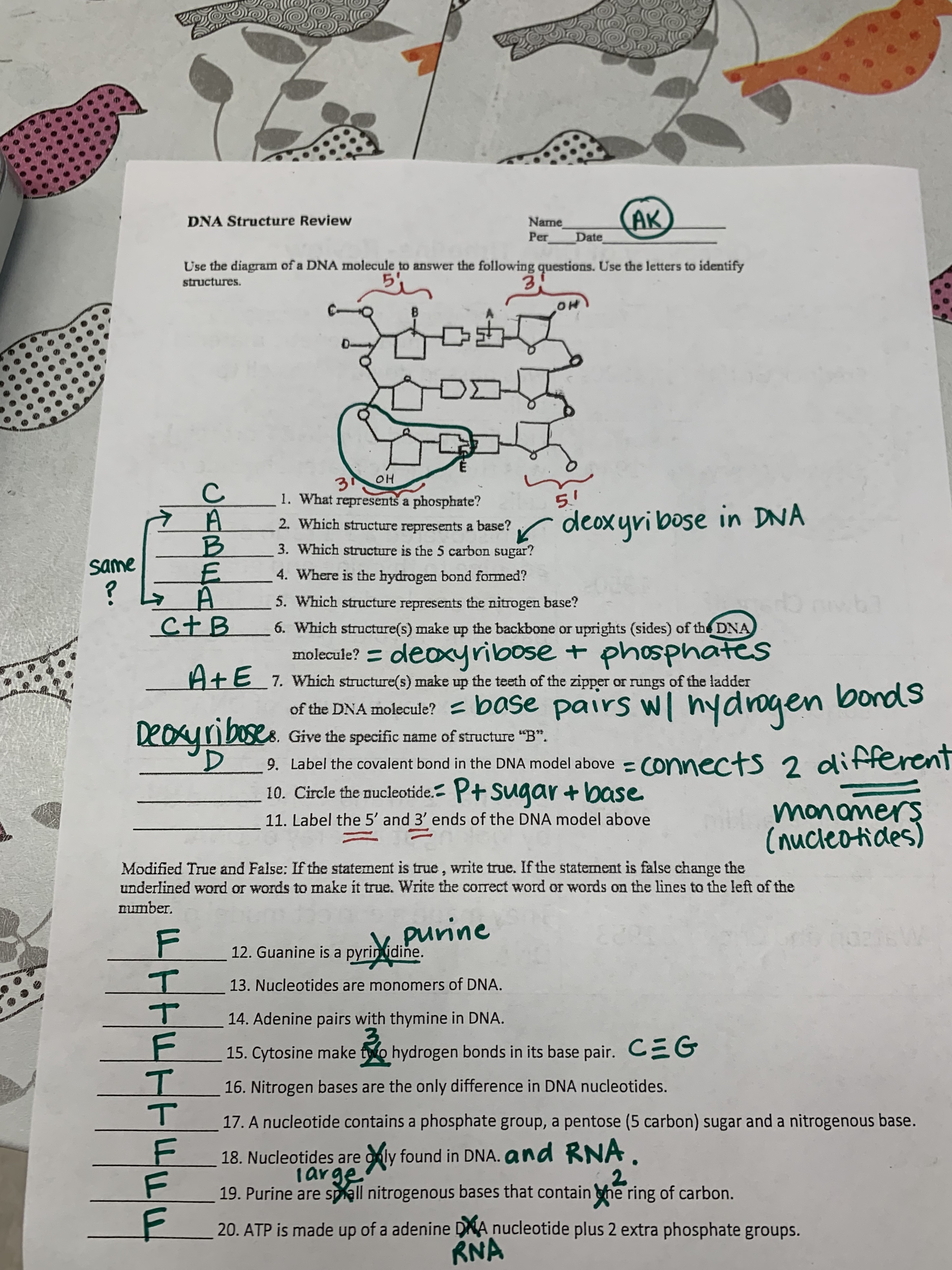
Image: www.onlineworksheet.my.id
Imagine this: Inside each cell of your body, there’s a library filled with volumes of information, each one meticulously recording the instructions for building and maintaining your entire being. This library is called DNA, and the way its volumes are organized, the structure of DNA, is what allows us to access and interpret this precious information.
The Building Blocks of Life
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a long, complex molecule composed of repeating units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made up of three parts:
- A sugar molecule: This is a five-carbon sugar called deoxyribose.
- A phosphate group: This is a negatively charged molecule, giving DNA its acidic nature.
- A nitrogenous base: This is the part that distinguishes one nucleotide from another. There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T).
Connecting the Nucleotides
These nucleotides join together to form a chain, with the phosphate group of one nucleotide linking to the sugar of the next. This chain creates a long, ladder-like structure. But what about the rungs of this ladder? This is where the nitrogenous bases come in.
The Double Helix: The Iconic Structure

Image: www.studypool.com
Pairing Up
The bases on one strand of DNA pair with bases on the other strand, forming the rungs of the ladder. This pairing is not random; it follows specific rules:
- Adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T): These two bases are held together by two hydrogen bonds.
- Guanine (G) always pairs with cytosine (C): These two bases are held together by three hydrogen bonds.
These complementary pairings are crucial for DNA’s stability and function.
The Significance of the Double Helix
The double helix structure of DNA is vital for the molecule’s ability to replicate (make copies of itself) and to store and transmit genetic information.
Replication: Pass the Code On
During replication, the two strands of DNA unwind, and each strand serves as a template for a new strand. The complementary base pairing ensures that each new strand is an exact replica of the original. This process allows every cell to inherit a complete set of genetic information, enabling growth, repair, and development.
Genetic Information: Encoding the Blueprint
The sequence of bases in DNA determines the genetic code. This code dictates the production of proteins, which are the building blocks of life. The order of bases in a gene (a specific segment of DNA) translates to a sequence of amino acids, which in turn determine the structure and function of the protein.
Unveiling the Secrets: Tools and Techniques
Scientists have developed sophisticated tools and techniques to study and manipulate DNA, furthering our understanding of its structure and function.
X-ray Diffraction: Capturing the Shape
The double helix structure of DNA was revealed in 1953 by James Watson and Francis Crick. They used X-ray diffraction images taken by Rosalind Franklin to deduce the molecule’s three-dimensional shape.
Genetic Sequencing: Reading the Code
Genetic sequencing is a process that determines the order of bases in a DNA molecule. This technology has revolutionized our understanding of DNA by allowing us to map the entire human genome.
DNA Beyond the Blueprint: A World of Applications
Our understanding of DNA has revolutionized various fields, from medicine to forensics.
Personalized Medicine: Tailor-Made Treatments
Scientists can now use genetic information to tailor treatments to individual patients, leading to more effective therapy and fewer side effects. DNA sequencing is widely used in drug development, genetic testing, and personalized cancer treatment.
Forensic Science: Unveiling the Truth
DNA has become a powerful tool in forensics. The unique combination of bases in each person’s DNA allows for accurate identification of individuals from biological evidence, playing a vital role in solving crimes.
Gene Editing: Rewriting the Code
Gene editing technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 allow scientists to alter the DNA sequence. This has potential applications in treating genetic diseases, developing new crops with enhanced traits, and even eradicating diseases like malaria.
The Ever-Expanding Knowledge of DNA
The study of DNA is a constantly evolving field. New discoveries and technologies are revealing the molecule’s fascinating complexity and its immense potential. From understanding the mechanisms of evolution to developing innovative therapies, DNA research promises to reshape our future in profound ways.
The Structure Of Dna Answer Key
Conclusion
The structure of DNA is a testament to the elegance and ingenuity of life. Its double helix structure encodes and transmits the genetic information that defines us, providing the blueprint for all living organisms. Understanding this structure has been a remarkable scientific feat, leading to a revolution in our understanding of life and opening doors to a future of personalized medicine, genetic engineering, and unprecedented possibilities. So next time you look at your reflection in the mirror, remember that you are staring at the embodiment of a complex and beautiful molecule, the very code of life itself.
Further Exploration:
- “The Double Helix” by James Watson: This book tells the fascinating story of the discovery of DNA’s structure.
- The National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI): This institute provides comprehensive information on human genetics, DNA, and related research.
- The Human Genome Project: This project aimed to sequence the entire human genome, a monumental achievement in scientific history.
Share your thoughts! Have you been fascinated by the structure of DNA? Share your experiences or questions in the comments below.






