I remember the time I was working on a crucial project, and a seemingly minor oversight—a delay in sourcing a key component—caused a ripple effect leading to missed deadlines and cost overruns. It was a stark reminder of how easily quality risks can emerge, even when we think we have everything under control. Quality management is not simply about preventing defects; it’s about systematically identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks that could jeopardize the success of any project or endeavor. This article delves into the intricate world of quality risks, exploring their sources, impact, and how to effectively manage them.
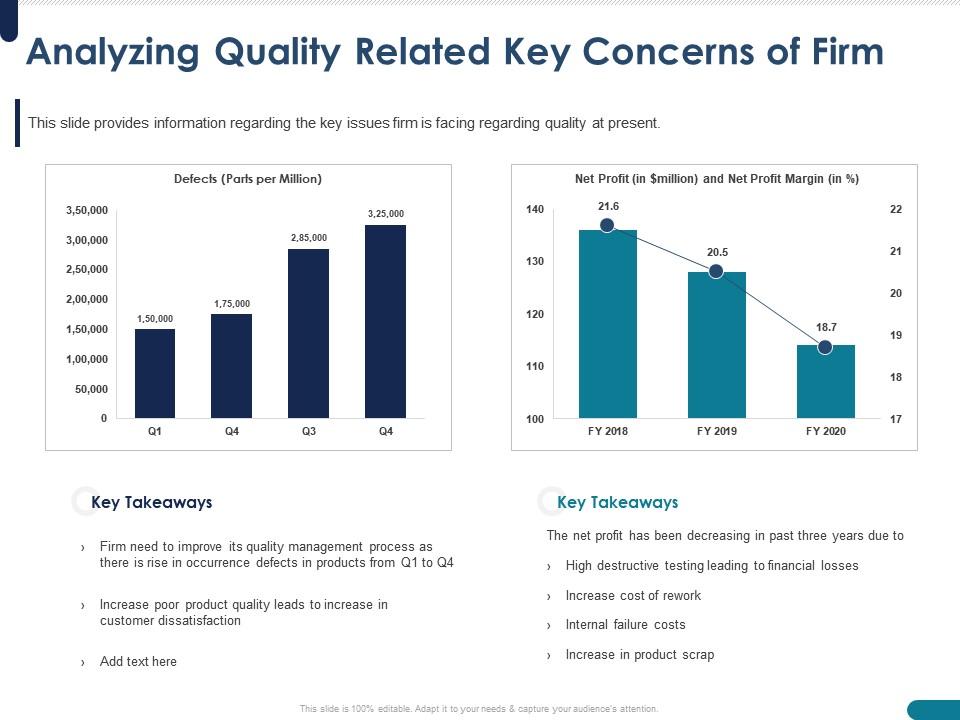
Image: www.slideteam.net
Quality risks, like any other risk, can significantly impact the success of a project or business. They can manifest in various forms, ranging from product deficiencies and customer dissatisfaction to regulatory non-compliance and reputational damage. It’s crucial to understand the root causes of these risks, as this knowledge empowers us to develop strategies for proactive prevention and mitigation.
Understanding Quality Risks
Definition and Scope
Quality risks encompass any potential threats or uncertainties that could negatively affect the quality of a product, service, or process. They can stem from various sources, including inadequate design, faulty materials, inadequate training, and inefficient processes. The scope of quality risks is broad, ranging from minor defects that might only disrupt individual customers to major failures that could lead to widespread recalls or even lawsuits.
Types of Quality Risks
Quality risks can be broadly categorized into:
- Product or Service Risks: These risks directly relate to the quality of the final product or service delivered to the customer. They could include design flaws, material defects, manufacturing errors, or inadequate testing.
- Process Risks: These risks stem from potential shortcomings within the operational processes leading to the production or delivery of the product or service. Inefficient workflows, inadequate training, or lack of proper documentation can contribute to process risks.
- System Risks: These risks are associated with the overall system within which the product or service is developed and delivered. Examples include outdated technology, inadequate infrastructure, or ineffective communication systems.
- Human-Related Risks: This category encompasses risks caused by human error, such as mistakes in design, production, or quality control. Lack of knowledge, inadequate training, or insufficient motivation can all contribute to human-related risks.

Image: www.slideshare.net
Impact of Quality Risks
Financial Consequences
Quality risks can have a significant financial impact on businesses. Cost overruns, rework, warranty claims, and product recalls are just a few examples. Inadequate quality control can lead to the production of defective products, resulting in waste and the need to replace faulty products.
Reputational Damage
In today’s digital world, word of mouth spreads quickly, and a company’s reputation is paramount. Quality risks can erode customer trust and confidence, resulting in decreased sales and brand loyalty. Negative online reviews, social media backlash, and media attention can further exacerbate the damage.
Regulatory Non-compliance
Many industries are subject to stringent regulations, and failure to meet quality standards can lead to hefty fines, penalties, and even lawsuits. Ensuring product safety and compliance with standards is crucial for any organization, particularly in industries like pharmaceuticals, food manufacturing, and medical devices.
Customer Dissatisfaction
The ultimate impact of quality risks is customer dissatisfaction. When customers receive products or services that do not meet their expectations, it can lead to complaints, returns, and even negative word-of-mouth. Maintaining customer satisfaction is essential for any business’s long-term success.
Managing Quality Risks
Risk Identification and Assessment
The first step in managing quality risks is to identify and assess them. This involves conducting a comprehensive analysis to determine potential areas where quality issues could arise. Brainstorming, risk assessments, and failure analysis techniques can assist in this process.
Risk Mitigation
Once risks are identified, the next step is to develop strategies to mitigate them. This may involve implementing process improvements, investing in training, adopting new technologies, or strengthening quality control procedures. The goal is to reduce the likelihood of the risk materializing or to minimize its impact if it does occur.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Quality management is not a one-time event; it requires continuous monitoring and improvement. This involves regularly reviewing quality data, analyzing trends, and refining processes to proactively address potential issues. It’s essential to stay adaptable and willing to make adjustments as needed to maintain optimal quality and minimize risks.
Latest Trends in Quality Management
In today’s dynamic environment, quality management is constantly evolving to address new challenges and leverage emerging technologies. Some key trends include:
- Data-Driven Insights: Organizations are increasingly using data analytics to gain deeper insights into quality performance, identify patterns, and proactively address potential issues.
- Digital Transformation: Automation, artificial intelligence, and other digital tools are being employed to streamline quality management processes, improve efficiency, and enhance decision-making.
- Customer-Centric Approach: The focus is shifting towards meeting and exceeding customer expectations. Companies are incorporating customer feedback into their quality management systems to ensure products and services are aligned with customer needs.
- Agile Methodology: Agile principles are being adopted in quality management, emphasizing flexibility, rapid iteration, and continuous improvement. This approach helps organizations respond quickly to changing market demands and customer expectations.
Tips for Effective Quality Risk Management
Effective quality management is not simply about adhering to checklist items but about fostering a culture of quality throughout the organization. Here are some key tips:
- Embed Quality into Every Stage: Quality should be integrated into every stage of product development, process execution, and customer interaction. This ensures a proactive approach to quality management.
- Invest in Training and Development: Employees are the backbone of any quality management system. Ensure they have the right knowledge, skills, and tools to perform their tasks effectively and meet quality standards.
- Foster Open Communication: Open feedback channels are essential for identifying and addressing quality issues proactively. Encourage employees to report concerns and participate in continuous improvement efforts.
- Embrace Technology: Embrace technology as a tool to improve quality management. Utilize digital platforms for data collection, analysis, and sharing, enabling efficient decision-making and process optimization.
- Focus on Continuous Improvement: Quality management is an ongoing journey. Continuously evaluate processes, seek feedback, and implement improvements to ensure ongoing effectiveness and minimize risks.
FAQ
Q: What are the most common quality risks in manufacturing?
A: Common manufacturing quality risks include: design flaws, material defects, process inconsistencies, inadequate quality control, and lack of training.
Q: How can I assess the impact of a potential quality risk?
A: You can assess the impact of a quality risk by considering its severity, likelihood, and consequences. A risk assessment matrix can help quantify the impact and prioritize mitigation efforts.
Q: What are some practical ways to improve quality communication within an organization?
A: Establish clear communication channels, use regular meetings, encourage open feedback, utilize digital tools for collaboration, and implement employee suggestion programs.
Which Of The Following Raises Quality Risks
Conclusion
Quality risks are an inherent part of any organization, but they can be effectively managed with a proactive approach. By identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks, companies can ensure they deliver products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations. It’s crucial to be vigilant and adapt to changing trends to maintain a culture of quality and minimize the impact of potential risks. Are you committed to building a culture of quality in your organization? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below.






