Ever found yourself stranded with a dead battery, a non-working radio, or headlights that refuse to illuminate? These are just a few of the electrical mishaps that can plague even the most reliable vehicles. And for a 1997 Dodge Dakota owner, understanding the fuse box and its diagram is crucial for tackling these issues.

Image: schematiclistneustadt.z19.web.core.windows.net
The fuse box acts as the electrical brain of your Dakota, protecting its delicate wiring and components from power surges and short circuits. It’s a system of fuses, each dedicated to a specific circuit, ensuring that a single malfunction doesn’t bring the entire vehicle to a halt. But with its intricate network of wires and components, finding the right fuse can be a daunting task. That’s where this guide steps in, providing an in-depth understanding of the 1997 Dodge Dakota fuse box diagram and its intricacies.
Navigating the 1997 Dodge Dakota Fuse Box
The 1997 Dodge Dakota comes with two primary fuse boxes: the under-hood fuse box located in the engine compartment, typically near the battery, and the interior fuse box situated on the driver’s side of the dashboard, underneath the steering wheel. Each fuse box holds a specific set of fuses, which control different electrical components. Understanding the layout of both fuse boxes is essential for effectively diagnosing and resolving electrical issues.
The Under-Hood Fuse Box
The under-hood fuse box in a 1997 Dodge Dakota is responsible for powering essential components like the engine, headlights, and various sensors. It houses a variety of fuses, each with a designated amperage rating that determines how much current it can safely handle. Here’s a breakdown of some commonly found fuses under the hood and what they control:
- Fuse 1: Battery Feed Circuit — Controls the power supply to the battery and related accessories.
- Fuse 2: Ignition Circuit — Enables the ignition system and allows the engine to start.
- Fuse 3: Power Seat Circuit — Controls the power adjustment for driver and passenger seats.
- Fuse 4: Exterior Lamp Circuit — Powers the headlights, taillights, and other exterior lights.
- Fuse 5: Fuel Pump Circuit — Supplies power to the fuel pump, which delivers fuel to the engine.
- Fuse 6: Radio / Instrument Cluster — Powers the radio, instrument gauges, and other electronic displays.
The Interior Fuse Box
The interior fuse box in your 1997 Dakota manages the electrical components within the cabin, including the power windows, door locks, and audio system. It’s conveniently located within the driver’s side dashboard for easy access. Some of the key fuses in the interior fuse box include:
- Fuse 1: Horn Circuit — Operates the vehicle’s horn.
- Fuse 2: Power Window Circuit — Provides power to the power windows.
- Fuse 3: Front Door Locks — Controls the power locks for the front doors.
- Fuse 4: Radio & Amplifier Circuit — Powers the radio and any external amplifiers.
- Fuse 5: Rear Window Defroster — Regulates the electrical heating element for the rear window.
- Fuse 6: Cigarette Lighter Circuit — Powers the cigarette lighter and other accessory outlets.
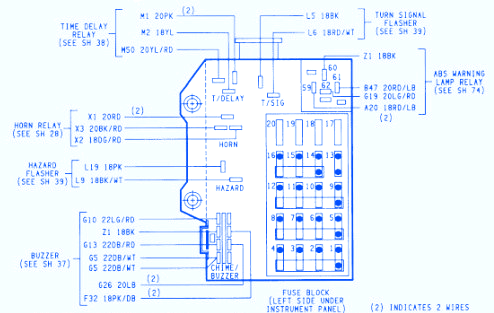
Image: specsdodgenew.blogspot.com
Interpreting the Fuse Box Diagram
The fuse box diagram is your roadmap to understanding the intricate electrical system of your Dakota. It visually maps out the location of each fuse and identifies the circuit it controls. This diagram is typically found within the owner’s manual or readily available online. Understanding the layout of the diagram is crucial for efficient troubleshooting.
Most fuse box diagrams follow a standard format. They usually feature a graphical representation of the fuse box itself, depicting the location of each fuse. Each fuse is assigned a number, which corresponds to its position within the box. The diagram also includes a key or legend that lists each fuse number, its amperage rating, and the circuit it controls. This information is indispensable when you need to identify which fuse is responsible for a particular malfunctioning component.
Common Fuse Problems and Troubleshooting
Fuse issues are a common occurrence due to electrical surges, short circuits, or wear and tear. If you suspect a blown fuse, here is a checklist to follow:
- Identify the Affected Circuit: Determine which component is not working, e.g., headlights, radio, power windows. This will help you pinpoint the relevant fuse.
- Locate the Fuse: Using the fuse box diagram, locate the fuse responsible for the specific circuit.
- Inspect the Fuse: Visually inspect the fuse. If it’s blown, the wire inside the fuse will be broken, leaving a visible gap.
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage. Never use a fuse with a higher amperage rating, as it can create a fire hazard.
- Test the Circuit: After replacing the fuse, test the circuit to see if the component is now working. If the problem persists, there might be a deeper electrical fault.
Replacing Fuses: A Step-by-Step Guide
Replacing a blown fuse is a simple task that any DIY enthusiast can handle. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Locate the Fuse Box: Identify the location of the fuse box, either under the hood or inside the cabin.
- Locate the Fuse: Use the fuse box diagram to determine the location of the specific fuse you need to replace. Each fuse is labeled with a number and amperage rating.
- Extract the Old Fuse: Use a fuse puller tool or a pair of tweezers to carefully remove the old blown fuse.
- Insert the New Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage. Ensure that the fuse is properly seated in the fuse holder.
- Test the Circuit: Once you’ve replaced the fuse, test the circuit to ensure that the affected component is now working.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring More Complex Electrical Issues
While replacing fuses is a fundamental skill for any car owner, some electrical issues might require more in-depth troubleshooting. For instance, if you’ve replaced a fuse and the problem persists, you may have a shorted wire or a faulty electrical component. In such cases, it’s crucial to seek professional assistance from a qualified automotive technician. They can use specialized tools and diagnostics to pinpoint the underlying problem, prevent further damage, and ensure a safe and reliable repair.
1997 Dodge Dakota Fuse Box Diagram
The Power of Your 1997 Dodge Dakota: Mastering Electrical Troubleshooting
Understanding the workings of the fuse box diagram and basic troubleshooting techniques can empower you to maintain a safe and functional driving experience with your 1997 Dodge Dakota. By familiarizing yourself with the fuse box and its parts, you’ll be equipped to handle common electrical issues and ensure the longevity of your vehicle. From addressing a blown head lamp to tackling a frustrating radio malfunction, this knowledge will equip you to confidently conquer any electrical challenge.
Remember, safety is paramount. Always prioritize caution while working with electronics and never hesitate to consult a professional if you’re unsure or encounter complex electrical problems. Your 1997 Dodge Dakota deserves the best care, and a thorough understanding of its electrical system is an important step towards ensuring its smooth operation and your peace of mind.






