Imagine this: you’re cruising down the highway, enjoying the open road, when suddenly, your 1996 Dodge Ram van’s headlights flicker and die. Panic sets in, and you’re left stranded, wondering what went wrong. This scenario, or something similar, has likely happened to many van owners, and it often boils down to a simple electrical issue. Luckily, with the right knowledge and a little patience, you can navigate the complexities of your van’s fuse box and tackle these electrical problems head-on.
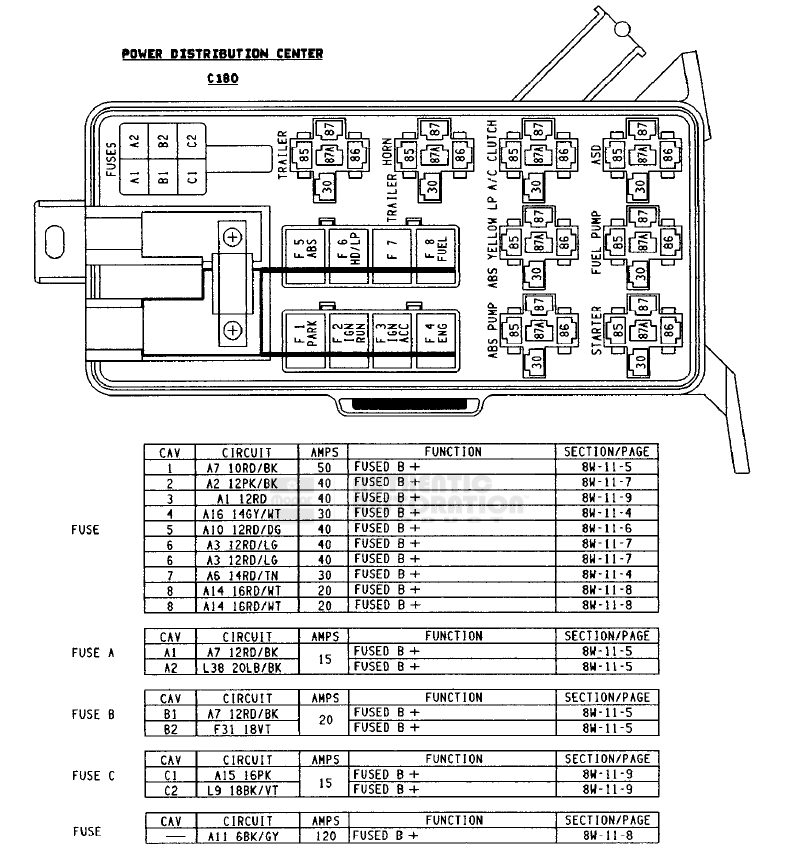
Image: mydiagram.online
This guide will unlock the secrets of your 1996 Dodge Ram van fuse box diagram, offering a comprehensive understanding of its functions and how to use it. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a novice driver, this article will equip you with the tools and knowledge to diagnose and potentially solve electrical issues in your van, saving you time and money in the long run.
Understanding the 1996 Dodge Ram Van Fuse Box: Your Electrical Lifeline
Your 1996 Dodge Ram van’s fuse box serves as a critical component in managing the flow of electrical power throughout your vehicle. It’s essentially a “circuit breaker” system, designed to protect important electrical components from damage caused by short circuits or overloads. Think of it as a mini-control center for your van’s electrical system.
Locating the Fuse Box: A First Step Towards Electrical Mastery
The 1996 Dodge Ram van boasts two fuse boxes, each with its designated functions:
-
Under-the-hood fuse box: This one, typically located under the hood near the battery, houses fuses responsible for the basic functionalities of the van, such as headlights, taillights, horn, and engine components.
-
Passenger compartment fuse box: Situated inside the vehicle, usually on the driver’s side dashboard, this fuse box controls electrical accessories like power windows, radio, and interior lights.
Decoding the Fuse Box Diagram: A Key to Electrical Success
The fuse box diagram, often included in your van’s owner’s manual or readily available online, acts as a roadmap, guiding you through the labyrinth of individual fuses and their specific functions. It presents a visual representation of each fuse, its corresponding amperage rating, and its designated circuit.
For example, you’ll find entries like “Headlights” or “Radio” listed alongside their corresponding fuse numbers and ampere ratings. Use this diagram to quickly identify the fuse responsible for any electrical issue you’re facing.
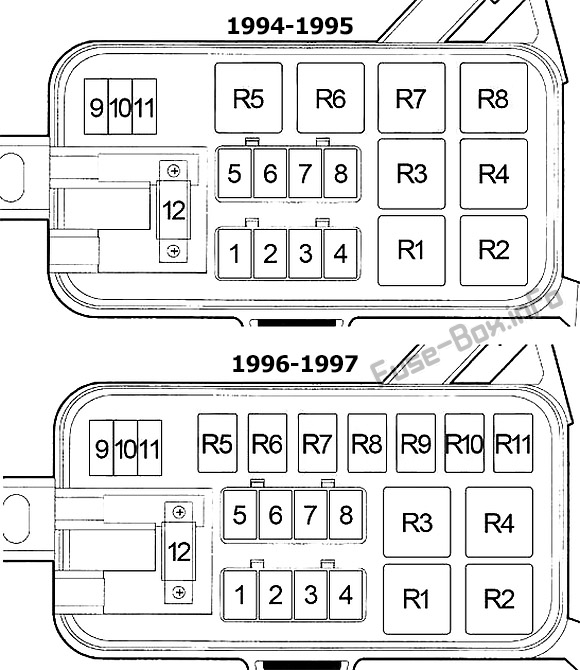
Image: wireengineeggers.z13.web.core.windows.net
Using the Diagram to Diagnose Issues: A Step-by-Step Guide
Once you’ve located your fuse box and obtained its diagram, troubleshooting becomes a less daunting task. Here’s a step-by-step process to help you pinpoint the root cause of electrical problems:
-
Identify the affected circuit: Determine which electrical component or system is malfunctioning. Is it the headlights, radio, or something else?
-
Locate the corresponding fuse: Refer to the fuse box diagram to find the fuse responsible for that specific circuit.
-
Visually inspect the fuse: Using a fuse puller, carefully remove the suspected fuse. Look for signs of damage, such as a blown fuse, which will appear as a melted or severed wire inside the fuse.
-
Test the fuse with a multimeter: If visual inspection doesn’t reveal damage, use a multimeter set to continuity mode to confirm whether the fuse is conducting electricity properly. A working fuse will show continuity, while a blown fuse will not.
-
Replace the blown fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Never use a higher amperage fuse, as it can overload the circuit and cause further damage.
Beyond Fuses: A Deeper Look into Electrical Troubleshooting
While blown fuses are a frequent culprit in electrical dramas, other factors can also contribute to electrical problems. These include:
-
Loose connections: Loose connections can prevent proper electrical flow, causing flickering lights, intermittent signals, or complete loss of power.
-
Wiring issues: Damaged or frayed wiring can result in short circuits, electrical fires, and other hazards. If you suspect wiring problems, seek the help of a qualified mechanic.
-
Faulty electrical components: A faulty alternator, battery, or other electrical component can lead to electrical malfunctions. Have these components inspected and replaced if necessary.
Expert Insights on Electrical Safety: Preventing Problems Before They Arise
Keeping your 1996 Dodge Ram van’s electrical system in top shape isn’t just about fixing problems; it’s about preventing them from occurring in the first place. Here’s what electrical experts recommend:
-
Regular maintenance: Conduct routine inspections of your fuse box, checking for loose connections, signs of corrosion, or any blown fuses.
-
Use the correct fuses: Always replace blown fuses with ones that have the same amperage rating specified in the fuse box diagram.
-
Preventative measures: Avoid overloading electrical circuits by minimizing the use of multiple power-hungry accessories at the same time.
1996 Dodge Ram Van Fuse Box Diagram
Empowering You with Electrical Confidence
Mastering your 1996 Dodge Ram van’s fuse box diagram is a crucial step towards taking control of your vehicle’s electrical health. By understanding its structure, utilizing it for troubleshooting, and practicing preventative measures, you can avoid costly repairs and ensure your van remains reliable and safe on the road. Remember: the key to a smooth journey lies in knowing your van’s electrical system – and that knowledge starts with the fuse box diagram.






